Fichier:Deep water wave.gif
Ce fichier provient de Wikimedia Commons et peut être utilisé par d'autres projets. Sa description sur sa page de description est affichée ci-dessous.
Description
| DescriptionDeep water wave.gif |
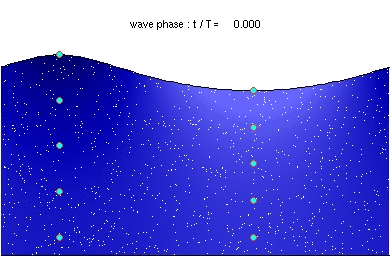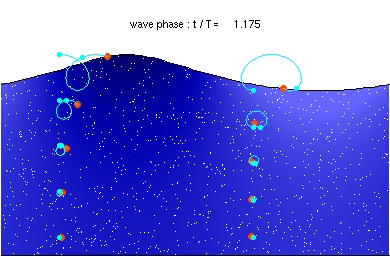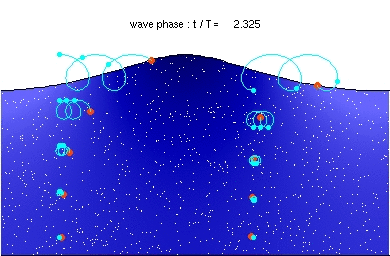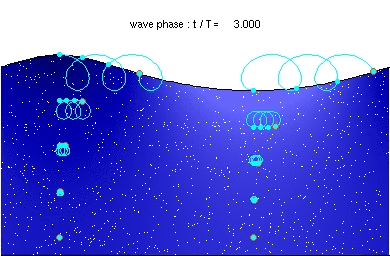
English: Stokes drift in deep water waves, with a wave length of about twice the water depth. The ratio of wave height to wavelength is H/λ=0.092. [1]
Description of the animation: The red circles are the present positions of massless particles, moving with the flow velocity. The light-blue line gives the path of these particles, and the light-blue circles the particle position after each wave period. The white dots are fluid particles, also followed in time. In the case shown here, the mean Eulerian horizontal velocity below the wave trough is zero. Observe that the wave period, experienced by a fluid particle near the free surface, is different from the wave period at a fixed horizontal position (as indicated by the light-blue circles). This is due to the Doppler shift. The wave physics are computed with the Rienecker & Fenton (R&F) streamfunction theory; for a computer code to compute these see: J.D. Fenton (1988) "The numerical solution of steady water wave problems". Computers & Geosciences 14(3), pp. 357–368. The animations are made from the R&F results with a series of Matlab scripts and batch files.Deutsch: Stokes Drift in Tiefwasserwellen mit einer Wellenlänge gleich der doppelten Wassertiefe. Beschreibung der Animation: Die roten Punkte bezeichnen die augenblicklichen Positionen der masselosen Teilchen, die sich mit der Strömungsgeschwindigkeit bewegen. Die hellblaue Linie ist die Bahnlinie dieser Teilchen und die hellblauen Punkte bezeichnen die Partikelpositionen nach jeder Wellenperiode. Die weißen Punkte sind gleichzeitig bewegte Flüssigkeitsteilchen. Im gezeigten Fall ist die mittlere horizontale Euler-Geschwindigkeit unter dem Wellental Null. Man beachte, dass sich die Wellenperiode der Flüssigkeitsteilchen nahe der freien Oberfläche von derjenigen bezüglich einer festen Position (bezeichnet durch die hellblauen Punkte) unterscheidet. Dies ist auf die Doppler-Verschiebung zurückzuführen. |
| Date | |
| Source | Travail personnel |
| Auteur | Kraaiennest |
| Autres versions |
|
| GIF information InfoField |
Conditions d’utilisation

|
Vous avez la permission de copier, distribuer et modifier ce document selon les termes de la GNU Free Documentation License version 1.2 ou toute version ultérieure publiée par la Free Software Foundation, sans sections inaltérables, sans texte de première page de couverture et sans texte de dernière page de couverture. Un exemplaire de la licence est inclus dans la section intitulée GNU Free Documentation License.http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
- Vous êtes libre :
- de partager – de copier, distribuer et transmettre cette œuvre
- d’adapter – de modifier cette œuvre
- Sous les conditions suivantes :
- paternité – Vous devez donner les informations appropriées concernant l'auteur, fournir un lien vers la licence et indiquer si des modifications ont été faites. Vous pouvez faire cela par tout moyen raisonnable, mais en aucune façon suggérant que l’auteur vous soutient ou approuve l’utilisation que vous en faites.
- partage à l’identique – Si vous modifiez, transformez ou vous basez sur cet élément, vous devez distribuer votre contribution sous une license identique ou compatible à celle de l’original.
Légendes
Éléments décrits dans ce fichier
dépeint
Valeur sans élément de Wikidata
12 janvier 2008
Historique du fichier
Cliquer sur une date et heure pour voir le fichier tel qu'il était à ce moment-là.
| Date et heure | Vignette | Dimensions | Utilisateur | Commentaire | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| actuel | 20 janvier 2008 à 14:44 |  | 390 × 256 (4,15 Mio) | wikimediacommons>Kraaiennest |
Utilisation du fichier
La page suivante utilise ce fichier :